
The spark plug has two primary functions:
Spark plugs carry electrical energy and turn fuel into working energy. A sufficient amount of voltage must be supplied by the ignition system to spark across the spark plug's gap. This is called "Electrical Performance." The temperature of the spark plug's firing end must be kept low enough to prevent pre-ignition, but high enough to prevent fouling. This is called "Thermal Performance", and is determined by the heat range selected.It's important to remember spark plugs do not create heat, they only remove heat. The spark plug works as a heat exchanger by pulling unwanted thermal energy away from the combustion chamber, and transferring the heat to the engine's cooling system. The heat range is defined as a plug's ability to dissipate heat.
The rate of heat transfer is determined by:
A spark plug's heat range has no relationship to the actual voltage transferred through the spark plug. Rather, the heat range is a measure of the spark plug's ability to remove heat from the combustion chamber. The heat range measurement is determined by several factors;
The insulator nose length is the distance from the firing tip of the insulator to the point where insulator meets the metal shell. Since the insulator tip is the hottest part of the spark plug, the tip temperature is a primary factor in pre-ignition and fouling. Whether the spark plugs are fitted in a lawnmower, boat, or a race car, the spark plug tip temperature must remain between 500C-850°C. If the tip temperature is lower than 500°C, the insulator area surrounding the center electrode will not be hot enough to burn off carbon and combustion chamber deposits. These accumulated deposits can result in spark plug fouling leading to misfire. If the tip temperature is higher than 850°C the spark plug will overheat which may cause the ceramic around the center electrode to blister and the electrodes to melt. This may lead to pre-ignition/detonation and expensive engine damage. In identical spark plug types, the difference from one heat range to the next is the ability to remove approximately 70°C to 100°C from the combustion chamber. A projected style spark plug firing tip temperature is increased by 10°C to 20°C.
NGK spark plug codes generally consist of six fields, which break down as follows:
| D | Size of the thread, pitch and hex |
|---|---|
| P R | The contruction shape or feature |
| 9 | Heat Rating |
| E | Thread Reach |
| A | Type of firing end contruction |
| - | - |
| 9 | Spark Plug Gap - not all plugs show this |
Some fields (e.g., the second field) are optional, and some fields may have multiple letters.
Back to top| Thread Diameter | Pitch | Hex | |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | 18mm | 1.50mm | 25.4mm |
| B | 14mm | 1.25mm | 20.8mm |
| C | 10mm | 1.00mm | 16.0mm |
| D | 12mm | 1.25mm | 18.0mm |
| E | 8mm | 1.00mm | 13.0mm |
| G | PF 1/2" pipe | 23.8mm | |
| AB | 18mm | 1.50mm | 20.8mm |
| BC | 14mm | 1.25mm | 16.0mm |
| BK | 14mm | 1.25mm | 16.0mm |
| DC | 12mm | 1.25mm | 16.0mm |
| BM_A | 14mm | 1.25mm | 19.0mm |
| BPM_A | 14mm | 1.25mm | 19.0mm |
| CM_6 | 10mm | 1.00mm | 14.0mm |
| Feature | |
|---|---|
| M | Compact(hex 19mm) |
| L | Short |
| P | Projected insulator |
| R | Resistor |
| U | surface or semi-surface discharge |
| Z | inductive suppressor |
Letters may be combined
Back to Symbols
From 2 (hot) through to 14 (cold) - for more information see Hot and Cold Plugs.
Back to Symbols
| Thread Reach | |
|---|---|
| E | 19.0mm |
| H | 12.7mm |
| L | 11.2mm |
| EH | Part Threaded |
| Total reach = 19.0mm | |
| Thread = 12.7mm | |
| BM_A | 9.5mm |
| B_LM | 9.5mm |
| CMR_A | 9.5mm |
| Firing and Construction | |
|---|---|
| C | short ground electrode |
| F | tapered seat |
| G | fine-wire center electrode, nickel |
| J | 2 ground electrodes (special shape) |
| K | 2 ground electrodes (Toyota) |
| -L | half heat range |
| -LM | insulator length: 14.5mm |
| M | insulator length: 18.5mm |
| -N | special ground electrode |
| P | platinum tip |
| Q | 4 ground electrodes |
| R | delta ground electrode |
| S | super copper core |
| T | 3 ground electrodes |
| V | fine-wire centre electrode, gold palladium |
| VX | platinum centre electrode |
| W | tungsten electrode |
| X | booster gap |
| Y | v-grooved centre electrode with extra projection |
| Spark Gap (pre-set) | ||
|---|---|---|
| 8 | 0.8mm | 0.032" |
| 9 | 0.9mm | 0.036" |
| 10 | 1.0mm | 0.040" |
| 11 | 1.1mm | 0.044" |
| 13 | 1.3mm | 0.050" |
| 14 | 1.4mm | 0.055" |
| 15 | 1.5mm | 0.060" |
| 20 | 2.0mm | 0.080" |
| none | Standard Gap | |
Heat rating and heat flow path of NGK Spark Plugs
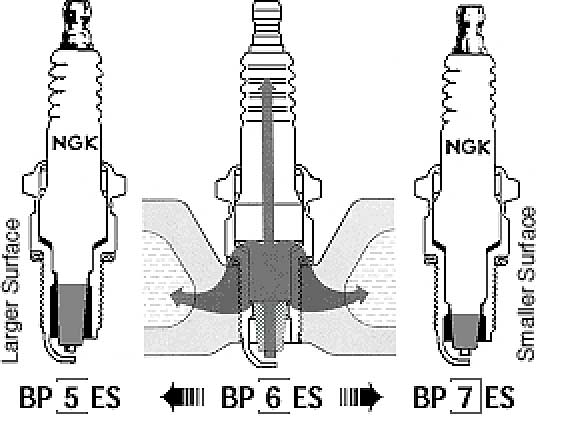
It has a larger surface exposed to the combustion gasses, it dissipates heat slowly, its firing end heats up quickly
It has a smaller surface exposed to the combustion gasses, it dissipates heat quickly, its firing end does not heat up quickly
The lower the number hotter the plug
The insulator nose length is the distance from the firing tip of the insulator to the point where insulator meets the metal shell. Since the insulator tip is the hottest part of the spark plug, the tip temperature is a primary factor in pre-ignition and fouling. Whether the spark plugs are fitted in a lawnmower, boat, or a race car, the spark plug tip temperature must remain between 500C-850°C. If the tip temperature is lower than 500°C, the insulator area surrounding the center electrode will not be hot enough to burn off carbon and combustion chamber deposits. These accumulated deposits can result in spark plug fouling leading to misfire. If the tip temperature is higher than 850°C the spark plug will overheat which may cause the ceramic around the center electrode to blister and the electrodes to melt. This may lead to pre-ignition/detonation and expensive engine damage. In identical spark plug types, the difference from one heat range to the next is the ability to remove approximately 70°C to 100°C from the combustion chamber. A projected style spark plug firing tip temperature is increased by 10°C to 20°C.
 |
Normal Condition
An engine's condition can be judged by the appearance of the spark plug's firing end. If the firing end of a spark plug is brown or light gray, the condition can be judged to be good and the spark plug is functioning optimally. |
 |
Dry and Wet Fouling
Although there are many different cases, if the insulation resistance between the center electrode and the shell is over 10 ohms, the engine can be started normally. If the insulation resistance drops to 0 ohms, the firing end is fouled by either wet or dry carbon. |
 |
Overheating
When a spark plug overheats, deposits that have accumulated on the insulator tip melt and give the insulator tip a glazed or glossy appearance. |
 |
Deposits
The accumulation of deposits on the firing end is influenced by oil leakage, fuel quality and the engine's operating duration. |
 |
Breakage
Breakage is usually caused by thermal expansion and thermal shock due to sudden heating or cooling. |
 |
Aged
A worn spark plug not only wastes fuel but also strains the whole ignition system because the expanded gap (due to erosion) requires higher voltages. Normal rates of gap growth are as follows: Four Stroke Engines: 0.01~0.02 mm/1,000 km (0.00063~0.000126 inches/1,000 miles) Two Stroke Engines: 0.02~0.04 mm/1,000 km (0.000126~0.00252 inches/1,000 miles) |
 |
Abnormal Erosion
Abnormal electrode erosion is caused by the effects of corrosion, oxidation and reaction with lead - all resulting in abnormal gap growth. |
 |
Melting
Melting is caused by overheating. Mostly, the electrode surface is rather lustrous and uneven. The melting point of nickel alloy is 1,200~1,300°C (2,200~2,400°F). |
 |
Erosion, Corrosion and Oxidation
The material of the electrodes has oxidized, and when the oxidation is heavy it will be green on the surface. The surface of the electrodes are also fretted and rough. |
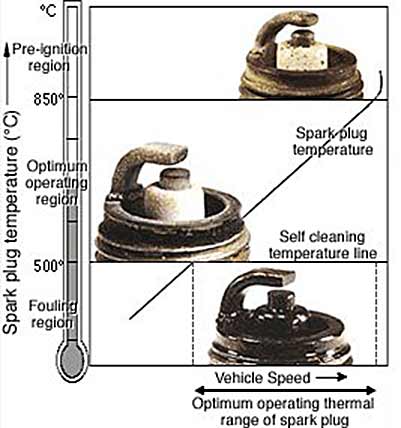
The firing end appearance also depends on the spark plugs tip temperature. There are three basic diagnostic criteria for spark plugs: good, fouled and overheated. The borderline between the fouling and optimum operating regions (500 degrees centigrade) is called the spark plug self-cleaning temperature. The temperature at this point is where the accumulated carbon and combustion deposits are burned off.
Keep in mind the insulator nose length is a determining factor in the heat range of a spark plug, the longer the insulator nose, the less heat is absorbed, and the further the heat must travel into the cylinder head water jackets. This means the plug has a higher internal temperature and is said to be a hotplug. A hot spark plug maintains a higher internal operating temperature to burn off oil and carbon deposits and has no relationship to spark quality or intensity.
Conversely, a cold spark plug has a shorter insulator nose and absorbs more combustion chamber heat. This heat travels a shorter distance and allows the plug to operate at a lower internal temperature. A colder heat range is necessary when the engine is modified for performance, subjected to heavy loads, or is run at a high rpm for a significant period of time. Colder spark plugs remove heat quicker, reducing the chance of pre-ignition/detonation. Failure to use a cooler heat range in a modified application can lead to spark plug failure and severe engine damage.
Start by using either a bicycle tire pump or an air compressor and pump a few bursts of air to rid the spark plug area of dirt, dust or gravel. Alternatively, clean off the old plug and the area around it with a rag or small paint brush. These steps help prevent any foreign material from falling down into the cylinder when the old plug is removed.
OK, time to set the gap of the new plug with a spark plug gap gauge (Remember the proper gap is specified in your manual). With your feeler gauge slide the correct thickness wire or feeler between the inner and outer electrodes at the tip of the plug. The feeler will slide between the electrodes with a slight drag when the plugs are properly gapped. If the gap isn't right, slightly bend the outer electrode until you achieve the right gap. Ensure the outer electrode is inline over the inner electrode.
Next, have a look at the cylinder head threads. Are they in good condition, clean, and free of dirt? New spark plug should freely screw into the cylinder head by hand. Any binding of the plug is an indication of debris or damage in the thread. TIP: lube the plug threads with a little grease or spray lubricant before you install them, this will make for an easier removal at your next spark plug change.

Spark Plug Engine Head Threadsaver 12mm
Spark Plug Engine Head Threadsaver 14mm
The Thread Saver does what its name implies... it saves threads. This unique tool was designed for one purpose and that is to clean or repair damaged spark plug port hole threads.
The ThreadSaver comes in two sizes, for the most popular range of spark plugs, 12mm and 14mm and is suitable for plain or tapered plug seat types. All you need to use it is a 5/8" spark plug socket or spanner. ThreadSaver will save you time and money.
The ThreadSaver is a collapsible tap with a centre rod that enables the user to regulate the amount of pressure at the thread cutting end of the tool. It enables the user to adjust the cutting depth of the thread by simply pushing the rod toward the cutting head to increase depth or retracting the rod to reduce cutting depth.
To start the operation, the expanding rod is removed. This allows the collapsible tap end to be inserted into the spark plug porthole. Bearing in mind this unique tool cleans or cuts the thread on the way out. With the collapsible tap end, the tool is inserted past the damaged or contaminated spark plug thread. The expanding rod is replaced through the centre of the ThreadSaver tool and now comes the best part, the ThreadSaver is wound out cleaning or repairing and realigning the thread and with the help of a little grease on the tap end, metal and carbon particles are brought out through the spark plug porthole along with the ThreadSaver tool.
The ThreadSaver is a cheap investment, is simple, and is fast and easy to use. It will go a long way in assisting to reduce lost labour time on a fairly common workshop problem when replacing spark plugs. A tool that every technician should have, ThreadSaver works on cast iron and alloy cylinder heads, can be used on cars, trucks, motorcycles, marine, lawn mowers, chainsaws or anything that uses a 12mm or 14 mm spark plug